 Dielectric Radomes
Dielectric Radomes
|
Maximum Protection Minimum Transmission Loss |
|
 Antennas for Communications (AFC) high technology radome capability combines the expertise of materials science, geodesic domes, structures and electromagnetics. AFC manufactures four types of dielectric radomes. The four types identify themselves primarily by the radome wall construction. In each case, the dielectric panel edges are reinforced into flanges for adjacent panel assembly. The panel flanges form a framework commonly called a Dielectric Space Frame (DSF) radome. Depending on radome wall structure, the adjacent panel flange framework may also serve as environmental load bearing beams or struts. Each panel is a molded one piece unit without bonds or seam lines. When assembled to the other panels, the panel array forms a truncated spherical surface. Individual panels may be doubly curved or flat yielding a faceted geodesic or spherical smooth appearance.
Antennas for Communications (AFC) high technology radome capability combines the expertise of materials science, geodesic domes, structures and electromagnetics. AFC manufactures four types of dielectric radomes. The four types identify themselves primarily by the radome wall construction. In each case, the dielectric panel edges are reinforced into flanges for adjacent panel assembly. The panel flanges form a framework commonly called a Dielectric Space Frame (DSF) radome. Depending on radome wall structure, the adjacent panel flange framework may also serve as environmental load bearing beams or struts. Each panel is a molded one piece unit without bonds or seam lines. When assembled to the other panels, the panel array forms a truncated spherical surface. Individual panels may be doubly curved or flat yielding a faceted geodesic or spherical smooth appearance.
Foam insulation is often added to the wall producing a 2 or 3-layer sandwich configuration. As required by sophisticated electrical performance requirements, inductive elements (wire, metallic strips etc.) may be inserted into the dielectric flanges to reduce scattering loss. The superior performance and advantages of DSF Radome technology are evident in the worldwide Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS), weather satellite and radar, air surveillance radar and Intelsat communications.
| The four DSF radome types are: |
|
| Maximum Environmental Protection | Minimum Transmission Loss |
|
|
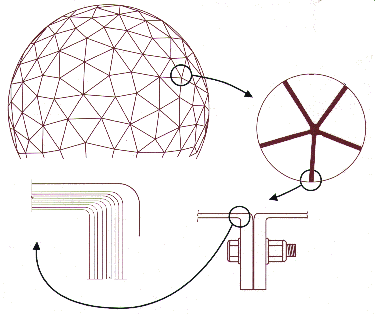 |
AFC engineers have developed a family of dielectric space frame radomes based on a range of required radome diameters. A set of radomes within a given range of radii will have identical panel count, panel shape and overall geometric layout. Individual panel size and the flange angles, which are radius dependent, will differ to accommodate the radome's overall shape factors. Spherical truncation is also radome specific, and is accommodated by sub panels unique to each requirement.
Radome accessories customize a radome to suit particular requirements. Accessories may include lightning protection, obstruction lights, ventilation, base collar, personnel door, indoor lights and power kits, hydrophobic coating and impedance matching. AFC has combined its extensive experience in fiberglass antenna manufacturing with its radome experience to produce the dielectric space frame radome. DSF radomes combine strength and weather resistance with minimal effect on microwave frequency signals. |
Monolithic Segments
 AFC's thin membrane wall dielectric space frame radomes are constructed of flat panel segments which combine a composite multi-layer polyester window with a fiberglass frame in one monolithic piece. DSF radome panel frameworks are completely inside so there is nothing to trap water in puddles or to launch ice adhesion. The only metal parts are stainless steel nuts and bolts holding the panel segments together. There are no metal components on the outside of the radome to corrode in hash environments or to discolor or stain radome panels. Without corrosion oxide induced diode mixers, DSF radomes are virtually intermodulation product free in the presence of modern multi-carrier communication systems and radars. The only exterior maintenance required is an occasional washing to remove dirt. No air pressure is required to support the radome. Even without pressurizing the radome, the polyester panel windows are pretensioned to minimize audible flutter, microphonics or "oil canning". Sandwich DSF panels add an internal low density closed cell foam and skin layer forming a thicker 2-layer or 3-layer wall. 3-layer sandwich panels are very rigid. They may be molded into spherical doubly curved or flat surface shaped panel units. For flat DSF panels, such as used in the thin membrane wall geodesic radome, the entire exterior of the radome is covered with TEDLAR ®. Tedlar is a unique long-lasting material with a proven weather resistant 20 year lifetime. Curved panel shapes use gelcoat as the exterior surface. An optional hydrophobic coating may be applied to either the gelcoat or Tedlar surface. This hydrophobic coating causes water to bead and run off in rivulets instead of sheeting. Hydrophobicity also serves as effective anti-ice protection for the radome and reduces rain related transmission loss.
AFC's thin membrane wall dielectric space frame radomes are constructed of flat panel segments which combine a composite multi-layer polyester window with a fiberglass frame in one monolithic piece. DSF radome panel frameworks are completely inside so there is nothing to trap water in puddles or to launch ice adhesion. The only metal parts are stainless steel nuts and bolts holding the panel segments together. There are no metal components on the outside of the radome to corrode in hash environments or to discolor or stain radome panels. Without corrosion oxide induced diode mixers, DSF radomes are virtually intermodulation product free in the presence of modern multi-carrier communication systems and radars. The only exterior maintenance required is an occasional washing to remove dirt. No air pressure is required to support the radome. Even without pressurizing the radome, the polyester panel windows are pretensioned to minimize audible flutter, microphonics or "oil canning". Sandwich DSF panels add an internal low density closed cell foam and skin layer forming a thicker 2-layer or 3-layer wall. 3-layer sandwich panels are very rigid. They may be molded into spherical doubly curved or flat surface shaped panel units. For flat DSF panels, such as used in the thin membrane wall geodesic radome, the entire exterior of the radome is covered with TEDLAR ®. Tedlar is a unique long-lasting material with a proven weather resistant 20 year lifetime. Curved panel shapes use gelcoat as the exterior surface. An optional hydrophobic coating may be applied to either the gelcoat or Tedlar surface. This hydrophobic coating causes water to bead and run off in rivulets instead of sheeting. Hydrophobicity also serves as effective anti-ice protection for the radome and reduces rain related transmission loss.
Low Transmission Loss
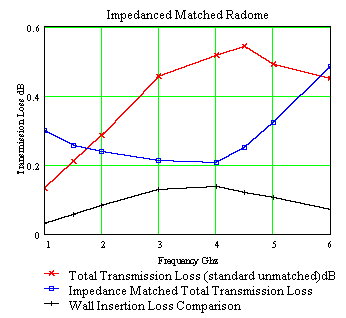
Radome transmission loss is composed of two major loss contributions. The first and usually the smallest contribution is the ordinary insertion loss of a microwave signal passing through the radome wall. The second and largest contribution is the scattering loss off the radome panel framework blocking the antenna aperture. Scattering loss is typically 4 to 10 times larger than the wall insertion loss. The use of a dielectric space frame greatly reduces the scattering loss associated with metal frames. This reduces the transmission loss, beam distortion and boresight error that can be caused by a metal frame. Use of a dielectric frame also eliminates the Faraday cage effect which inhibits the use of metal space frame radomes at lower frequencies. Every DSF radome exhibits the RF property that the total transmission loss, scattering plus wall insertion loss, approaches zero dB at low frequencies (as opposed to metal space frame radomes, whose loss increases without limit. This property is important for UHF/VHF emergency radio communications contained within the radome).
Virtually Invisible
|
The dielectric space frame radome is divided into several large sections. To eliminate the possibility of coherent scattering from panel framework blocking the antenna, the sections are divided into random sizes of triangular segments. Combining the sections produces a pseudo-randomly segmented radome which has proven to be virtually invisible to microwave scattering.
Scattering loss can also be greatly reduced in a dielectric space frame radome by a process known as impedance matching. The capacitive reactance of the radome framework is removed by adding properly spaced wires into the frame. The inductance of the wires impedance matches, "tunes out", the capacitance of the radome framework to reduce the scattering loss and the phase distortion with its associated boresight shift and sidelobe perturbation. The use of stainless steel hardware with a dielectric space frame avoids any dissimilar metal contact which can produce intermodulation distortion. |
Simple Installation
AFC dielectric space frame radomes can be quickly assembled in the field using normal hand tools. They can be assembled around existing antenna equipment or assembled and then lifted and set over the equipment.
AFC can provide erection crews for a turnkey project or supervisors for customer installation. Because air pressure is not required to support the radome, several lower panels can be easily removed to permit large pieces of equipment or vehicles to be added or removed. A temporary header kit provides stability to the structure.
AFC has the in-house tooling capabilities and computer aided design techniques to quickly and economically produce custom dielectric space frame radomes to meet any thin membrane l-layer, 2-layer or 3-layer sandwich requirements.
| Membrane | PRETENSIONED POLYESTER LAMINATE |
| Sandwich Wall | INTERNAL CLOSED CELL FOAM CORE |
| Exterior Surface | TEDLAR ® OR GELCOAT |
| Air Pressure | NONE REQUIRED |
| Maintenance | ROUTINE CLEANING |
| Design Life | 20 YEARS |
| Equatorial Diameter | Base Diameter | Radome Height | Center Height | Number of Panels | ||||
| (meters) | (feet) | (meters) | (feet) | (meters) | (feet) | (meters) | (feet) | |
| 2.3 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 7.5 | 3.0 | 10.0 | 1.5 | 5.0 | 4 |
| 3.7 | 12 | 2.7 | 8.9 | 3.0 | 10.0 | 1.2 | 4.0 | 6 |
| 5.5 | 18.0 | 3.9 | 12.7 | 4.7 | 15.4 | 1.9 | 6.4 | 12 |
| 8.0 | 26.4 | 6.5 | 21.4 | 6.4 | 21.0 | 2.4 | 8.0 | 55 |
| 9.5 | 31.0 | 6.5 | 21.4 | 7.8 | 25.7 | 3.1 | 10.2 | 55 |
| 10.7 3-Layer Sandwich or Solid Laminate |
35 3-Layer Sandwich or Solid Laminate |
8.3 | 27.3 | 8.7 | 28.5 | 3.3 | 11.0 | 110 |
| 10.7 Dielectric Radome Any DSF Type |
35 Dielectric Radome Any DSF Type |
8.7 | 28.4 | 8.6 | 28.3 | 3.2 | 10.6 | 165 |
| 12.6 | 41.4 | 8.8 | 28.7 | 10.9 | 35.6 | 4.5 | 14.9 | 160 |
| 14.9 | 48.8 | 11.4 | 37.3 | 12.2 | 40.2 | 4.8 | 15.9 | 275 |
| 15.8 | 52.0 | 12.1 | 39.7 | 13.0 | 42.8 | 5.1 | 16.8 | 275 |
| 18.6 | 61.0 | 14.0 | 45.9 | 15.4 | 50.6 | 6.1 | 20.1 | 275 |
| 20.7 | 68.0 | 16.2 | 53.1 | 16.8 | 55.2 | 6.5 | 21.2 | 430 |
| 21.5 | 70.5 | 17.3 | 56.8 | 17.1 | 56.1 | 6.4 | 20.9 | 430 |
| 23.0 | 75.5 | 19.3 | 63.2 | 17.8 | 58.4 | 6.3 | 20.7 | 430 |
| 29.6 | 97.1 | 23.7 | 77.7 | 23.7 | 77.7 | 8.9 | 21.3 | 860 |
| 33.5 | 110.0 | 23.0 | 75.5 | 28.9 | 94.8 | 12.4 | 39.8 | 1100 |
| Other custom sizes available. These radomes are available as standard dielectric or as impedance matched dielectric radomes. |
||||||||
AFC manufactures, markets and sells worldwide satellite dish antennas, conical horn antennas, radomes, antenna feeds, microwave and waveguide components, ultra low loss waveguide transmission line TallGuide ®, and shelters. Our customers serve the broadcast, communications, radar, weather and cable industry, defense, government, and government agencies worldwide.
A complete Internet WWW AFC document index may be found in Antennas for Communications (AFC) Home Page Document Summary List. Additional radome information is described within AFC's Radome Capability Brochure, Dielectric Space Frame Radome Advantages, AFC's Proprietary Hydrophobic Coating Data Sheet , 5.5 Meter (18 ft.) Diameter Radome Brochure and Application Note for Radome Thermal Insulation.
Top of PageReturn to Radome Network Home Page
2499 SW 60th Ave, Ocala, FL 34474
Telephone (352)687-4121 Fax (352)687-1203 E-mail sales@afcsat.com
Tallguide is a Registered Trademark of Antennas for Communications
Tedlar is a Registered Trademark of Dupont.
Copyright © 1997 - 2000 Antennas for Communications